Deciding whether to use night vision or thermal imaging boils down to your circumstances. Thermal imaging detects heat and excels in total darkness, piercing through smoke or leaves. It’s unbeatable for spotting people or animals afar, under any light. Night vision, on the other hand, amplifies existing light, suited for dim conditions, not pitch black. It’s more wallet-friendly. Thermal imaging, with its superior detection in tough settings, costs more. Each shines in its way, so ponder your needs deeply. There’s much to uncover about leveraging their strengths for your scenarios.
Key Takeaways
- Thermal imaging shines in utter darkness and cuts through barriers like fog or smoke, offering unmatched clarity where light is absent.
- Night vision, more affordable, fits best when seeking improved sight in dim light, not pitch black.
- Deciding between night vision and thermal imaging hinges on particular demands, such as how far you need to see and the surroundings.
- Thermal imaging captures warmth, perfect for spotting living beings from afar, under various circumstances.
- Night vision amplifies available light, ideal for cityscapes or nights with a hint of moonlight, where some light exists.
Understanding Thermal Imaging
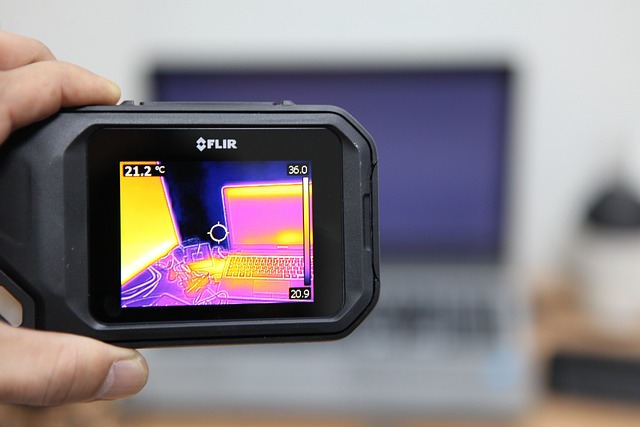
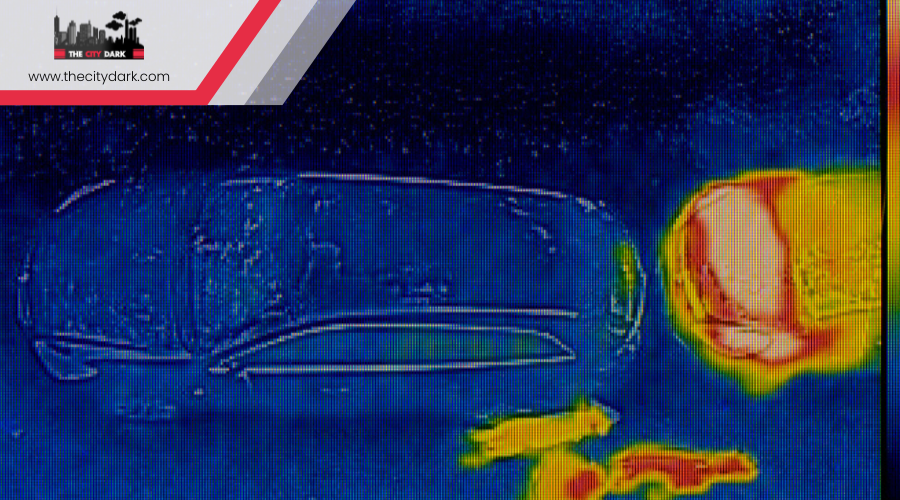
Thermal imaging allows you to see what’s usually invisible, capturing the heat that people, animals, and things give off, even in complete darkness. This technology uses sensors that pick up on far-infrared radiation—the heat from anything warm. This means you don’t need light to see with thermal vision; it works in broad daylight or the darkest night.
The power of thermal imaging is in showing heat signatures in simple shades of gray or bright colors, making it easy for you to see living beings or objects that are usually hidden. It can see through foliage or thin materials, showing you what’s behind them clearly.
Thermal imaging excels where regular night vision can’t. It cuts through fog, which normally blocks your view. That’s why it’s widely used in security, surveillance, and hunting. Thermal imaging gives you the ability to see where others can’t.
Basics of Night Vision
How does night vision let you see when it’s almost completely dark? It takes tiny bits of light and makes them much stronger, so you can see in the dark. Devices like night vision goggles and cameras do this with something called an image intensifier. This part takes light from the moon or stars and makes it bright enough for your eyes to see what’s usually hidden.
But, can you see with night vision when it’s completely dark? It’s not that simple. Night vision needs at least a little light to work. If there’s no light at all, these devices can’t do their job. It’s important to remember this, depending on where you want to use them.
Even with this limit, night vision is very useful. It changes the game in many areas, making it possible to work, watch wildlife, or keep places safe at night. This technology gives us the power to do things at night that we couldn’t do before, as long as there is a little bit of light.
Key Differences Highlighted
Experience the distinct contrasts between night vision and thermal imaging in a concise manner. We’ll delve into their range and the sharpness of their visuals. Grasping these nuances aids in choosing the right technology for you.
Detection Range Compared
When comparing night vision and thermal imaging, thermal imaging stands out. It sees heat from thousands of feet away. Night vision, however, reaches only a few hundred feet in the best conditions.
- Thermal imaging is superior for long distances.
- Night vision is for closer tasks.
- Fog or smoke affects thermal imaging less.
- Night vision needs some light, which limits its long-distance use.
These differences matter when choosing technology for your needs.
Imaging Clarity Differences
Understand the difference in clarity between night vision and thermal imaging to choose the right tool. Thermal cameras pick up slight temperature changes, as tiny as 0.01°C, and see radiation. This lets them make clear images from heat differences, perfect for seeing warm things against cool backgrounds. Night vision devices make images by making ambient light stronger but can lose clarity when light changes. They depend on visible light, so their image resolution isn’t as good as thermal imaging, which always gives clear views by showing objects’ heat. For detailed images, thermal imaging is the best choice.
Visibility in Complete Darkness
In total darkness, thermal imaging shines by sensing heat, whereas night vision needs some light. Understanding their differences is crucial in lightless environments. Thermal imaging excels in darkness, creating images from heat. Night vision, however, struggles without light, as it enhances existing light for visibility.
Consider these points:
- Thermal imaging captures heat from beings or machines, crucial for search and rescue or surveillance in dark conditions.
- Night vision devices falter in complete darkness, requiring ambient light or infrared illumination.
- Thermal imaging’s independence from light makes it superior in environments like dense forests or deep caves.
- Thermal imaging, relying on temperature differences, can see through smoke, fog, and some foliage, offering advantages in zero-light situations night vision cannot.
Analyzing Cost Implications
Night vision devices cost less than thermal imaging ones, making them a good choice for people watching their spending. This older technology works well for many night activities without costing too much. When looking into night vision or thermal imaging, thinking about the price is key. Night vision is a budget-friendly option that still performs well.
Thermal imaging, a newer tech, costs more. It sees heat from objects, letting you see in complete darkness, smoke, or bad weather. But, this top-notch feature means paying more at the start. The cost of thermal imaging devices is a big consideration, especially for those keeping an eye on expenses.
Choosing between night vision and thermal imaging means looking at what you can spend against what each technology offers. Night vision is cheaper, while thermal imaging has more advanced features but at a higher cost. Think about what matters most to you and how it fits your budget before deciding.
Dual-Use Potential
Night vision and thermal imaging offer great value beyond the military or surveillance, touching many aspects of life and work.
- Law Enforcement: Night vision helps with night surveillance and chases; thermal imaging finds people in smoke or behind cover.
- Wildlife Study: These tools let researchers watch nocturnal animals quietly, capturing their activities without interference.
- Maintenance in Industry: Thermal imaging spots parts that get too hot before they break, saving money and time.
- Search and Rescue: Thermal cameras find people in tough spots; night vision helps rescuers move in the dark.
These points show how night vision and thermal imaging are more than tools for the dark. They enhance safety, efficiency, and understanding in various fields.
Application Spectrums
Both night vision and thermal imaging excel in their own realms. Night vision needs some light and reveals details. Thermal imaging, on the other hand, shines in complete darkness, detecting heat. Knowing their strengths in different settings helps pick the right one.
Usage Environments
Exploring how night vision and thermal imaging are used shows their importance in areas like the military, firefighting, and medicine.
- Night vision technology works best in low light but not total darkness. It depends on some light to see better. Soldiers, police, and security use it when they need to see in different lighting.
- Thermal imaging shines in the dark by seeing heat differences. This is key for firefighters, rescuing people, and keeping machines running.
- Both are helpful in medicine too. They use thermal imaging to spot heat changes and night vision to see in dim light.
- Even though they work differently, both need light in some form to work right. This shows how they fit in various situations.
Target Identification Capabilities
When identifying targets, thermal imaging and night vision are key, each with unique strengths. Thermal imaging excels in spotting heat – humans, animals, vehicles – from afar, even through barriers or in total darkness. Night vision, preferred by the military and hunters, excels in recognizing and identifying targets clearly. While thermal imaging is superior for detection, night vision is better for recognition. Using both technologies together greatly enhances target identification, combining their strengths.
Advancements in Technology
Recent upgrades in technology have significantly enhanced thermal imaging and night vision, offering you better performance and new, complex features. These advancements have transformed these tools, providing clearer images, improved detection, and innovative features that increase their usefulness in various settings. Let’s examine some key improvements:
- Finer Thermal Cameras: Now, thermal cameras can spot temperature changes as tiny as 0.01°C, giving you detailed, sensitive thermal images.
- Clearer Night Vision: Advances in night vision have boosted image clarity and resolution, helping you see better in dim light.
- Thermal Devices with More Features: Today’s thermal imaging devices come with customizable color palettes, cutting-edge image processing, and better thermal sensitivity, making your viewing experience richer and more insightful.
- Night Vision with Augmented Reality: Night vision devices now incorporate augmented reality, overlaying digital data on the real world, greatly improving your awareness of your surroundings.
These technological leaps have not only enhanced the basic functions of thermal imaging and night vision devices but have also introduced features that broaden their use and effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Option
Choosing between night vision and thermal imaging depends on what you need and where you’ll use them. Night vision works well in light, perfect for cities or under the moon. Thermal imaging sees heat, great in total darkness or through fog and smoke.
Money matters too. Night vision is cheaper, good if you’re careful with spending. But, spending more on thermal imaging can pay off in tough situations.
Check local laws on these devices before you buy.
Future Prospects
Exploring the choice between night vision and thermal imaging unveils a promising future for these technologies. Their evolution will transform their utility across numerous fields.
Here’s a glimpse into the future:
- Clear, Detailed Images: Upcoming night vision devices will offer enhanced image quality and resolution. This will provide clearer, more detailed visuals, even in complete darkness.
- Augmented Reality Integration: Future devices may include augmented reality, overlaying real-time information on the night vision display. This could offer unparalleled awareness of one’s surroundings.
- Compact, Lightweight Designs: Efforts are underway to make these devices lighter and more compact. This will allow for the same advanced capabilities in a more manageable form.
- Advanced Image Processing: Incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning, night vision technology will become more intelligent. This means more efficient image processing and the ability to automatically adjust to different environments.
The advancements in night vision and thermal imaging technology are set to expand their capabilities significantly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Thermal Imaging Better Than Night Vision?
You are comparing technologies, considering visibility, cost, environmental effects, and durability. Thermal imaging often surpasses night vision in detection, despite higher costs and different environmental impacts.
What Is Better for Night Hunting Thermal or Night Vision?
For night hunting, thermal excels in spotting animals, unaffected by weather or surroundings. Often, its battery life outperforms, though it might not compete in cost with night vision, which provides good flexibility.
Does the Military Use Night Vision or Thermal?
The military employs both, guided by the need for simplicity and directness. They aim for authenticity, adapting to the environment and mission demands, always striving to ensure their narrative is true to the reality of warfare.
What Is the Disadvantage of Thermal Scope?
Thermal scopes cost a lot and can’t see far. Bad weather and needing much power trouble them. Also, their pictures might not be very clear.
Conclusion
Are you deciding between night vision or thermal imaging? Each has benefits. Night vision amplifies dim light, allowing you to see in darkness. Thermal imaging senses heat, showing objects in complete darkness. The cost differs; night vision often costs less. Your decision should depend on your needs and budget. Technology improves, making both choices more adaptable for future use.