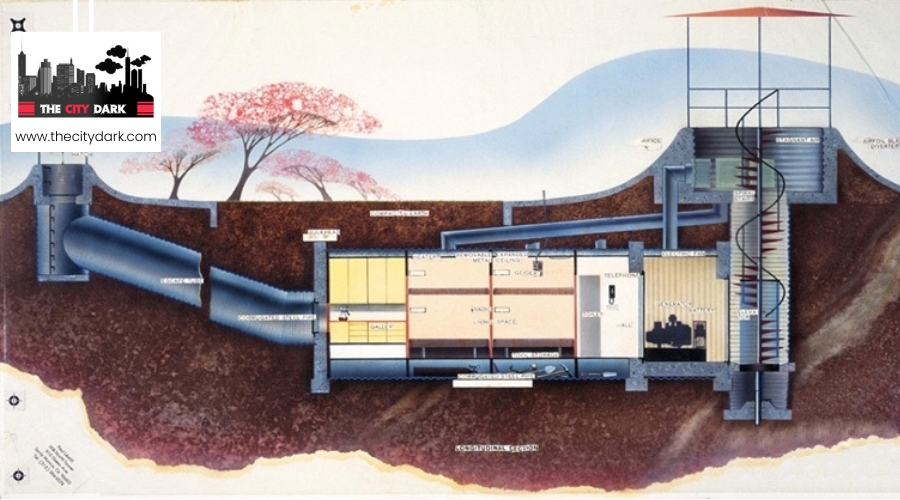
Imagine the earth trembling beneath your feet, the sky darkened by ominous clouds, signaling the need for immediate shelter from an unthinkable threat. As you contemplate the construction of a nuclear fallout shelter, you’re embarking on a journey that intertwines survival instinct with architectural savvy. You’ll need to consider various types of shelters, from underground bunkers to fortified above-ground structures, each with their unique advantages and challenges.
Selecting the right location becomes a puzzle of geography and accessibility, while the design must incorporate robust materials and innovative technologies to shield against radiation and ensure the air remains breathable. Essential living facilities, from water storage to sleeping quarters, must be meticulously planned to sustain life in a scenario where the outside world is temporarily unreachable.
With safety as your guiding principle, understanding the nuances of ventilation systems and radiation shielding becomes crucial. As we explore these aspects, you’ll discover the critical decisions that could make all the difference in a moment of crisis, inviting you to ponder the complexities of creating a haven against the unthinkable.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the different types of nuclear fallout and associated risks is crucial for designing an effective fallout shelter.
- Underground bunkers with robust air ventilation systems are the most effective shelters against nuclear fallout.
- Basements can be converted into fallout shelters with reinforced walls and proper ventilation.
- Above-ground bomb shelters, while less protective, can be fortified and equipped with ventilation systems.
Understanding Nuclear Fallout

To effectively plan for survival in the event of a nuclear explosion or reactor accident, it’s crucial you understand nuclear fallout, including how it spreads and its potential impacts on the environment and health. Nuclear fallout, the residual radioactive material propelled into the atmosphere following such catastrophic events, can travel vast distances. This contamination settles on the ground, endangering both the natural environment and human health.
Grasping the severity of nuclear fallout is vital when designing a fallout shelter. You’re not just building a bomb shelter; you’re crafting a haven to protect your safety and well-being from nuclear radiation. An underground shelter with robust air ventilation systems is essential to filter out fallout particles, ensuring you breathe clean air. Moreover, understanding the types of fallout and their associated risks helps in making informed decisions about your shelter’s location, design, and the necessary supplies to stockpile, including uncontaminated food and water.
Educating yourself about nuclear fallout’s impact allows for better preparedness, ensuring you can create a secure environment capable of sustaining life during such an unprecedented event.
Types of Fallout Shelters
Having understood the critical importance of nuclear fallout and its dangers, it’s now essential to explore the various types of fallout shelters available to ensure your protection. The right shelter can significantly reduce your exposure to harmful radiation and provide a safe haven during such perilous times.
Here’s a quick rundown of the options you’ve got:
- Underground Bunkers: These are perhaps the most effective shelters against nuclear fallout. Built below the earth’s surface, these bunkers often feature thick walls and are equipped with air filtration systems to prevent radioactive particles from entering. An air pump (KAP) is a critical component, ensuring a continuous supply of fresh air.
- Basement Fallout Shelters: If building a separate underground bunker isn’t feasible, converting your basement into a fallout shelter is a viable alternative. With the addition of reinforced walls and a proper ventilation system, your basement can serve as a safe room during nuclear fallout.
- Community Fallout Shelters: These shelters are larger, designed to accommodate multiple families or a community. They’re equipped with larger ventilation systems and multiple air pumps to cater to the higher occupancy.
- Above-Ground Bomb Shelters: While not as protective against radiation as underground options, above-ground bomb shelters can be fortified and equipped with ventilation systems to offer a degree of safety against nuclear fallout.
Choosing the Right Location
Selecting the optimal location for your fallout shelter involves careful consideration of several factors to ensure maximum safety and privacy. When planning your nuclear fallout shelter, choosing a safe and private location is crucial. You’ll want to steer clear of areas prone to flooding, fire, dense vegetation, or near utility lines. These can compromise the shelter’s integrity or accessibility.
Prioritize secrecy and safety by picking a spot near your home for quick access during emergencies. It’s wise to hide the construction process to keep it off your neighbors’ radar. Before you start building, call 811 to locate any underground utilities; this step can’t be overlooked to avoid any potential hazards.
Strategically position your bomb shelter to maximize protection against potential blasts, ensuring it’s easily reachable in a crisis. The chosen location should also allow you to build your shelter underground, offering additional protection from the fallout. Carefully evaluate the terrain to ensure the water levels are suitable and won’t damage your shelter.
Design and Blueprint Fundamentals
Now that you’ve pinpointed the perfect spot for your fallout shelter, it’s time to focus on selecting the right materials and optimizing your layout. You’ll need materials that aren’t only durable against the pressures of the earth but also efficient in maximizing your shelter’s space through smart design. These steps are crucial in ensuring your shelter is both safe and functional, avoiding any unnecessary setbacks during construction.
Selecting Shelter Materials
When designing your nuclear fallout shelter, carefully choosing the right materials is crucial for ensuring solid protection and longevity. Selecting shelter materials can seem daunting, but focusing on a few key aspects can guide you through the process, especially when the goal is to withstand a nuclear attack. Here’s what to consider:
- Concrete: Offers solid protection against blast and fallout; a staple in shelter design.
- Steel and Lead: Ideal for reinforcement and radiation shielding; crucial for underground bunkers.
- Insulation Materials: For temperature control inside; don’t overlook this when building one.
- Durability and Affordability: Balance these when selecting materials; it’s essential for stocking your shelter effectively.
Layout Optimization Techniques
To maximize your shelter’s functionality and safety, it’s essential to focus on layout optimization techniques that incorporate efficient space use and structural integrity. When it comes to bomb shelter design, adopting an open area plan and utilizing vertical storage are key for space utilization. Wall-mounted furniture not only saves space but also adheres to efficient design principles, ensuring each person has 5-10 square feet for comfort.
Selecting strong, waterproof materials like reinforced concrete enhances the structure designed for nuclear war survival skills. Incorporating instructions for building in plumbing systems is crucial for sanitation. Strengthening your bunker with reinforcing bars and blast-resistant materials is a testament to how Shelters Work, prioritizing both space efficiency and safety in the face of nuclear threats.
Construction Materials and Techniques
Now that you’ve got your design down, it’s crucial to pick the right materials and techniques for your fallout shelter. Concrete is your best bet for both the foundation and walls, offering unmatched protection and a cost-effective solution.
Next, you’ll need to consider how to shield your space effectively, focusing on emergency exits and proper ventilation to ensure safety and breathability.
Choosing Resilient Materials
Selecting resilient materials like reinforced concrete and steel is crucial for ensuring your nuclear fallout shelter offers both durability and protection. When you decide to build your shelter, the materials you choose are the most important thing to consider. They’re what stand between you and the aftermath of a nuclear disaster.
Here’s how to design a nuclear fallout shelter with peace of mind:
- Choose reinforced concrete and steel for their ability to withstand blasts and fallout.
- Incorporate insulation materials to maintain a stable internal temperature.
- Invest in high-quality concrete and steel reinforcement bars for added structural integrity.
- Select materials based on the required level of protection and your budget to ensure your shelter is both effective and affordable.
Effective Shielding Techniques
Effective shielding techniques, utilizing materials like concrete and steel, are essential for constructing a nuclear fallout shelter that ensures your safety.
Concrete offers sturdy and affordable protection against blast and fallout, while steel, lead, wood, and packed soil provide options based on your protection needs and budget.
Reinforce these materials with steel bars and add insulation to control temperature.
Plan for adequate space and ensure the shelter includes essential safety features like separate emergency hatches and efficient air intake and exhaust systems to maintain fresh air.
Don’t forget to stock up on essential supplies, ensuring water and air remain uncontaminated by nuclear particles or UV light.
Effective shielding also involves safeguarding utility lines to ensure your shelter remains a safe haven.
Essential Living Facilities
To ensure your survival and comfort in a nuclear fallout shelter, it’s crucial to include essential living facilities such as sleeping areas, dining space, and ample storage for supplies. These elements are vital for sustaining life during the period you’ll need to stay inside, away from the hazardous conditions outside.
Here are four key items to incorporate within your shelter:
- Ample Food and Water Supply: Stock up on nonperishable food items and ensure there’s enough bottled water for every person inside. Including a water filter can provide an additional layer of safety for your water supply.
- Medical Supplies and First-Aid Kit: Accidents or illnesses can happen, so having a well-stocked first-aid kit and essential medical supplies is critical.
- Comfortable Sleeping Areas: Ensure there’s enough room for every individual to have a comfortable sleeping area. This is important for rest and maintaining morale over extended periods.
- Dining and Living Space: Designate areas for eating and living to maintain a semblance of normalcy. These spaces are crucial for mental health and social interaction among those inside the shelter.
Including these facilities will significantly enhance your ability to safely and comfortably stay inside your shelter until it’s safe to emerge.
Ventilation and Filtration Systems
While ensuring your shelter is stocked with essential living facilities is crucial, you mustn’t overlook the importance of a robust ventilation and filtration system. In the event of a nuclear fallout, the air inside the shelter could become contaminated or stale, making it dangerous to breathe without proper ventilation and filtration systems in place.
To keep the air inside the shelter safe, consider installing air-intake and exhaust pipes at opposite ends. This setup ensures a continuous flow of fresh air, removing water vapor and other contaminants. An air pump is a popular option for actively moving stale air out and bringing fresh air in, especially when natural airflow is insufficient.
Keep in mind, the main entrance of your shelter should have a reliable filtration system to prevent radioactive particles from entering when you access the outside world. This system should be capable of filtering out not just radioactive particles but also dust and biological agents.
Stocking Your Shelter
You’ll need to ensure your shelter is stocked with essential supplies to keep you and your family safe and sustained during a nuclear fallout. Stocking your shelter is a crucial step in your preparedness plan, and there are key items you need to know to make sure you’re able to use your resources effectively. Keep it simple but comprehensive, focusing on the necessities that will take care of your basic needs.
Here are four essential items to stock in your shelter:
- Food Supplies: Stock up on nonperishable food items that have a long shelf life. Aim for a variety of foods to ensure a balanced diet. Make sure you have at least a three-month worth of food for every person.
- Clean Water: Store ample supplies of clean water for drinking, cooking, and hygiene. Consider water purification methods as well.
- First Aid Kit: Prepare a comprehensive first aid kit with necessary medications, medical supplies, and tools for any potential emergencies.
- Emergency Equipment: Install emergency lighting, backup power systems, and communication devices. Also, consider adding books, games, and other activities to maintain morale and mental well-being.
Maintenance and Safety Tips
Having stocked your shelter with essentials, it’s crucial to focus on maintenance and safety tips to ensure long-term sustainability and security. Regularly inspect the structure of your shelter, whether it’s in your home or office building, or even if it’s a more basic setup like a hole in the ground. This is key to keeping everyone inside as safe as possible.
The next step is to check and replace air filters and ventilation systems. Clean air is vital, so you’ll want to be sure to pack additional filters. Monitoring and restocking emergency supplies, including food, water, and medical supplies, is another critical task. It’s not enough to just DIG A TRENCH and forget; maintenance and safety tips require ongoing attention.
Don’t overlook the importance of conducting regular drills and training. Familiarity with safety protocols can make a significant difference in an emergency. Also, keep communication systems and backup power sources in top shape. Testing their functionality regularly ensures you’re prepared for any scenario.
It’s possible to build a secure shelter, but without proper maintenance and safety practices, its effectiveness is compromised.
Conclusion
In conclusion, designing a nuclear fallout shelter requires understanding the risks and implementing protective measures. Choose a strategic location and focus on sturdy construction materials and techniques. Don’t forget about essential living facilities and a robust ventilation system. Stock your shelter with necessary supplies and regularly check for maintenance needs.
By following these tips, you can ensure your safety and peace of mind in the event of a nuclear disaster. Stay prepared and stay safe.