You’re shining a light on the hidden world of wildlife with night vision for conservation. Thermal imaging and infrared technologies let researchers observe nocturnal creatures without disturbance. You track everything from small pollinators to large predators, learning about their habits, health, and threats. This technology is crucial in combating habitat destruction and poaching, notably saving rhinos in Kruger National Park. Despite challenges like weather and cost, the insights into nocturnal wildlife behaviors are invaluable for conservation. A vast nocturnal universe awaits your exploration.
Key Takeaways
- To observe animals at night without altering their behavior, researchers turn to night vision.
- This technology captures clear details of how wildlife interacts, eats, and uses their surroundings.
- It’s key in spotting and stopping poachers, especially in places like Kruger National Park.
- Using thermal imaging, the health and movement of at-risk species are closely watched.
- Night vision sheds light on how human actions affect animals of the night, guiding conservation efforts.
Monitoring Nocturnal Species
Monitoring nocturnal species is vital. These creatures, big and small, keep ecosystems healthy. Their lives, hidden by night, are threatened by human actions. In wildlife research, thermal imaging and similar technologies have changed how we study these hidden beings. Nocturnal animals, from small pollinators to large predators, balance nature in darkness. Their secretive ways make them vulnerable to change and human expansion.
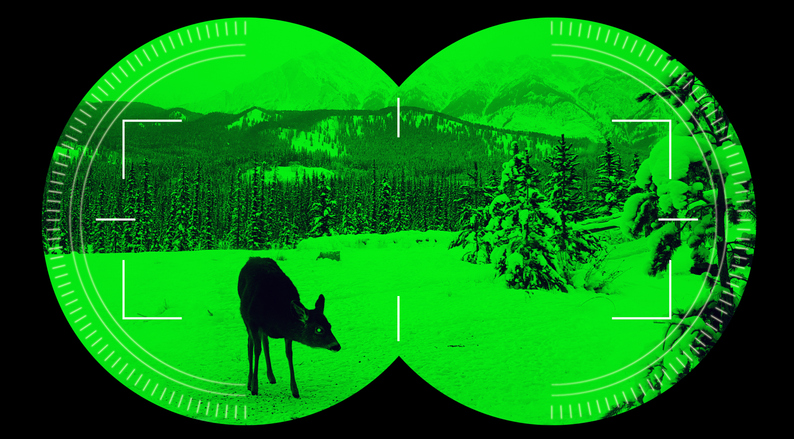
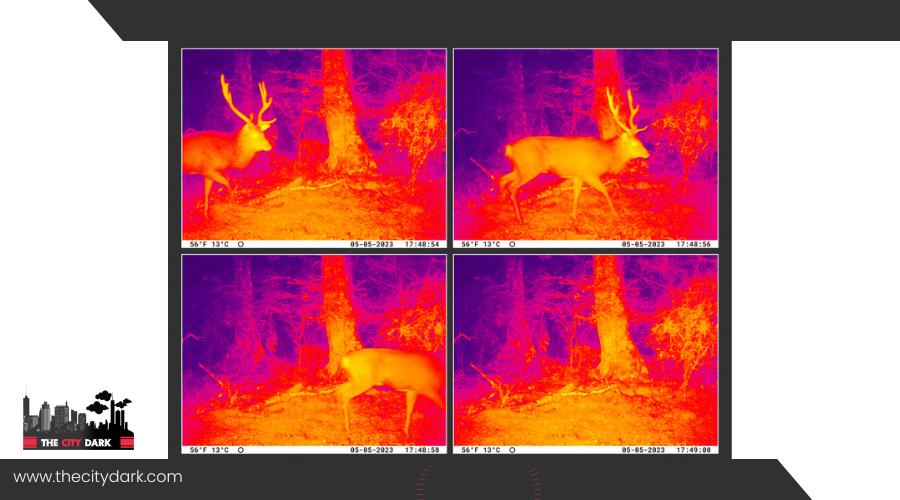
As a wildlife researcher, you use night vision to watch these creatures without altering their natural actions. Thermal imaging lets you see animals’ heat signatures, aiding in the study of their activities in complete darkness or tough environments. This technology is crucial for collecting precise data on endangered species, aiding conservation.
You’re gathering important data on nocturnal species’ habits, health, and threats. This information is key for creating protection strategies. Your work with night vision is vital for conservation, helping protect our planet’s nocturnal wildlife.
Night Vision Devices Overview
Understanding night vision devices in wildlife research enhances your ability to study nocturnal species. You have various tools, each with unique benefits for observing the night world. Image intensifier devices amplify light, providing high-resolution images for real-time observation. They are cost-effective, a favorite for budget-conscious researchers.
Infrared illuminator-assisted devices emit invisible light, improving visibility in complete darkness without disturbing nocturnal creatures. It’s like a secret window into their world.
For identifying species or capturing detailed information, turn to thermal imaging devices. They detect thermal radiation, offering insights otherwise missed, all without needing an IR illuminator.
These night vision devices are crucial in wildlife research. They enhance monitoring and data collection, significantly aiding the conservation of nocturnal species. By grasping the specifics of each device, you make informed research decisions, leading to accurate species identification and effective conservation efforts.
Advantages of Night Vision
Night vision technology greatly improves how researchers study nocturnal wildlife. This tool changes the way we observe animals at night. It lets us see animals that were once invisible in the dark. Night vision is not just about seeing in the dark; it helps us understand nocturnal creatures better.
Night vision helps us spot heat signatures. This feature gives clear insights into wildlife behavior and movement, unaffected by obstacles like dense foliage or shadows. It’s crucial for studying wildlife interactions, feeding habits, and how they use their habitats. Moreover, night vision is key for wildlife conservation. It helps gather detailed data that aids in protecting these animals.
Challenges in Night Vision Usage
While night vision technology brings big wins for wildlife study, it faces tough hurdles. One big challenge is how weather messes with your gear’s image quality. Using night vision to watch animals at night, you’ll find fog, rain, or deep darkness can blur what you see. These changing conditions are key in figuring out how well night vision works for saving wildlife.
Also, the cost of top-notch night vision gear is steep. Better gear that shows clearer images in bad weather costs more. Plus, keeping this gear in top shape adds extra work, especially in rough spots. These money and work issues are crucial in planning to watch animals at night without bugging them.
Getting these challenges is a must for anyone using night vision to help wildlife. It means, despite the hurdles, you can still watch and save animals effectively.
Case Studies in Conservation
Investigating conservation case studies highlights how crucial night vision technology is in combating poaching, especially in places such as Kruger National Park. Over 1,000 rhinos were poached last year, making the need for effective conservation tools clear. High-tech efforts, like the use of $20,000 heat-seeking drone cameras, mark a significant investment in wildlife protection. These devices, with thermal imaging and infrared cameras, let researchers watch wildlife clearly, without disturbing them.
The loss of the last male northern white rhino, leaving just two females, underscores the importance of this technology. It serves as a security system for nature, going beyond simple observation. It helps conservationists understand the movements and behaviors of endangered species, ensuring they are effectively monitored and protected.
The information gathered is not merely numerical; it shapes strategies to counter poachers’ changing tactics. Night vision and infrared tools have become essential in the ongoing fight for conservation, offering visibility in the dark to safeguard those unable to call for help.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Night Vision Work in Animals?
In animals, night vision is an adaptation. Eyes become more sensitive, better at seeing in the dark. Evolution sharpens these abilities for night hunting. They see infrared and distinguish colors, a result of their eyes’ evolution.
Which Animal Has the Best Night Vision?
You wonder which animal sees best at night? Owls. Their eyes, shaped by the hunt and night life, excel. Their evolution for night has sharpened their way through darkness.
Can Animals See in Complete Darkness?
You wonder, can animals see in pitch black? No, they cannot. They’ve evolved other senses, for night hunts and escaping predators, despite the challenge of seeing and city lights.
What Is It Called When Animals Can See in the Dark?
Animals that see in the dark have adapted for the night. They track predators, find prey, and survive better. This shows how vision and senses evolve based on need and environment.
Conclusion
To put it simply, night vision technology is changing wildlife conservation. It helps us watch and understand nocturnal animals, their homes, and dangers. Yes, it’s expensive and complex. But, the benefits, like watching without disturbing and getting better information, outweigh the problems. Looking at examples, night vision is more than a tool. It’s changing the game in saving our world’s wildlife. Thanks to technology’s ability to see in the dark, conservation has a hopeful future.