Biting Bugs and Disease: How to Protect Yourself in a Post-Disaster World

After a disaster strikes, most people focus on food, water, and shelter—but there's another threat that often gets overlooked: biting insects and the diseases they carry. In a post-disaster world, conditions like stagnant water, poor sanitation, and displaced populations create the perfect breeding ground for mosquitoes, ticks, and other pests.
These bugs can spread serious illnesses like malaria, dengue, Lyme disease, and West Nile virus. In this article, we’ll cover practical, effective ways to protect yourself from biting insects when medical help may be limited and prevention becomes your first line of defense.
| Category | Tips |
|---|---|
| Understanding Bug Risks | - Be aware of insect-borne diseases like Lyme, Zika, and West Nile. - Mosquitoes breed in standing water; ticks hide in tall grass and wooded areas. |
| Protective Clothing | - Wear long sleeves, pants, and light-colored, tightly woven fabrics. - Tuck pants into socks; tape cuffs in tick-prone areas. - Use permethrin-treated clothing for added protection. |
| Insect Repellents | - Choose EPA-approved repellents (DEET, Picaridin, or Oil of Lemon Eucalyptus). - Apply after sunscreen; reapply after swimming or sweating. - Use on exposed skin and clothing, avoiding eyes and mouth. |
| Bug-Free Environment | - Eliminate standing water weekly to prevent mosquito breeding. - Use screens on windows and doors; seal holes. - Keep spaces cool and ventilated; remove trash and debris. |
| Tick Safety | - Check yourself and pets after time outdoors. - Remove ticks with fine-tipped tweezers; clean the area after. - Watch for symptoms like rashes or fever and save the tick for testing. |
| Mosquito Management | - Avoid outdoor activities at dawn and dusk. - Use mosquito repellents and wear full coverage clothing. - Keep water containers emptied or covered. |
| Stings From Bees, Wasps, Hornets | - Stay calm and avoid swatting. - Remove bee stingers quickly; apply ice for swelling. - Monitor for allergic reactions like swelling or difficulty breathing. |
| Allergic Reactions | - Use antihistamines for minor reactions. - Be alert for signs of anaphylaxis—seek medical attention immediately. - Don’t ignore delayed symptoms; they may indicate complications. |
| Travel Tips | - Visit a travel clinic at least 6 weeks before departure. - Learn when and where insects are most active at your destination. - Always pack and use appropriate insect repellents. |
Understanding the Threat of Biting Bugs
While biting bugs might seem like just a nuisance, they actually pose serious health threats. Mosquitoes, ticks, and biting flies can transmit diseases like West Nile virus, Lyme disease, and Zika virus. These bites aren't just annoying; they can lead to significant health issues, especially in a post-disaster environment where these bugs thrive.
Mosquitoes, for instance, find ideal breeding conditions in standing water left by floods, increasing your risk of exposure to these diseases.
Being aware of insect behaviors and habitats is essential. Ticks hide in wooded areas and tall grass, while mosquitoes favor stagnant water.
Effective Clothing Strategies for Bug Bite Prevention
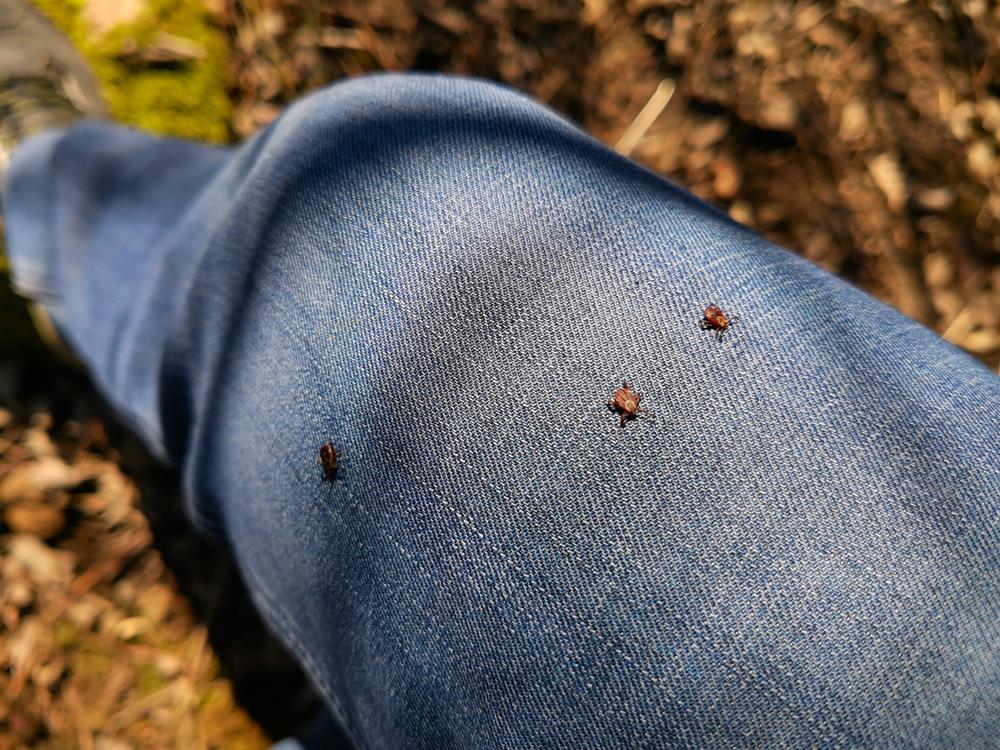

When venturing into bug-prone areas, choosing the right clothing can greatly reduce your risk of bites. Opt for light-colored, loose-fitting garments made from tightly woven materials like nylon or polyester. These fabrics prevent insects from penetrating while lighter shades deter bugs.
Always wear long sleeves and long pants, tucking them into socks or boots to create a barrier. Wearing permethrin-treated clothing offers extra protection, as this treatment repels insects effectively. Factory-treated garments remain potent throughout their lifespan.
Improve your safety by taping cuffs or tucking pants into socks, minimizing skin exposure. This is vital in tick-heavy areas such as grass and foliage. Cover as much skin as possible, which also aids in spotting and removing any ticks promptly.
Choosing and Using Insect Repellents
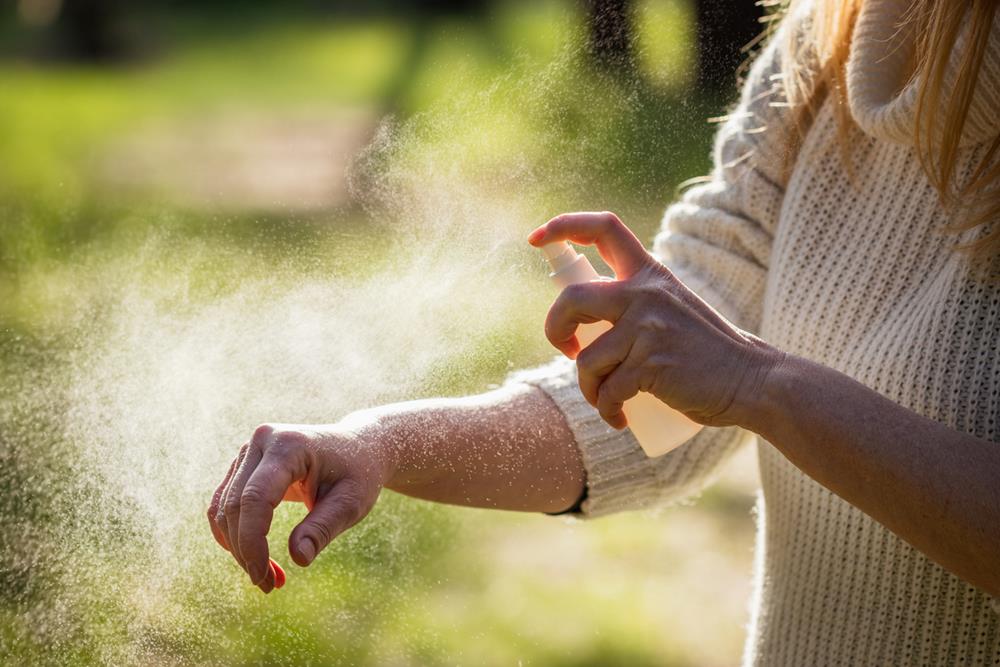

To effectively protect yourself from biting bugs, it’s crucial to choose and use the right insect repellents.
Opt for EPA-approved insect repellents with active ingredients like DEET, Picaridin, or Oil of Lemon Eucalyptus. These ingredients are proven to ward off bugs that can carry serious disease.
Confirm to apply the repellent evenly on exposed skin and clothing, avoiding eyes and mouth. After application, wash your hands to prevent accidental ingestion.
For best results, apply sunscreen initially, let it absorb, then apply the insect repellent.
Consider permethrin-treated clothing for long-lasting protection against ticks and mosquitoes.
Always follow the manufacturer's instructions, especially regarding reapplication after activities like swimming or sweating, to maintain continued protection.
Maintaining a Bug-Free Living Environment

Creating a bug-free living environment starts with proactive measures that keep pests at bay.
Begin by eliminating standing water weekly, as it’s a breeding ground for mosquitoes. Check and repair window screens regularly to guarantee they're tightly fitted and free of holes, preventing insect entry.
Keep indoor areas well-ventilated and use air conditioning; cooler temperatures can deter many biting bugs. Outside, clear debris and trash, which attract pests and offer hiding spots.
Indoors, consider using insect repellents with EPA-approved ingredients to reduce biting insects.
By taking these steps, you’ll effectively maintain a bug-free living environment, creating a safer and more comfortable space for you and your family.
Tick Prevention and Safe Removal Techniques
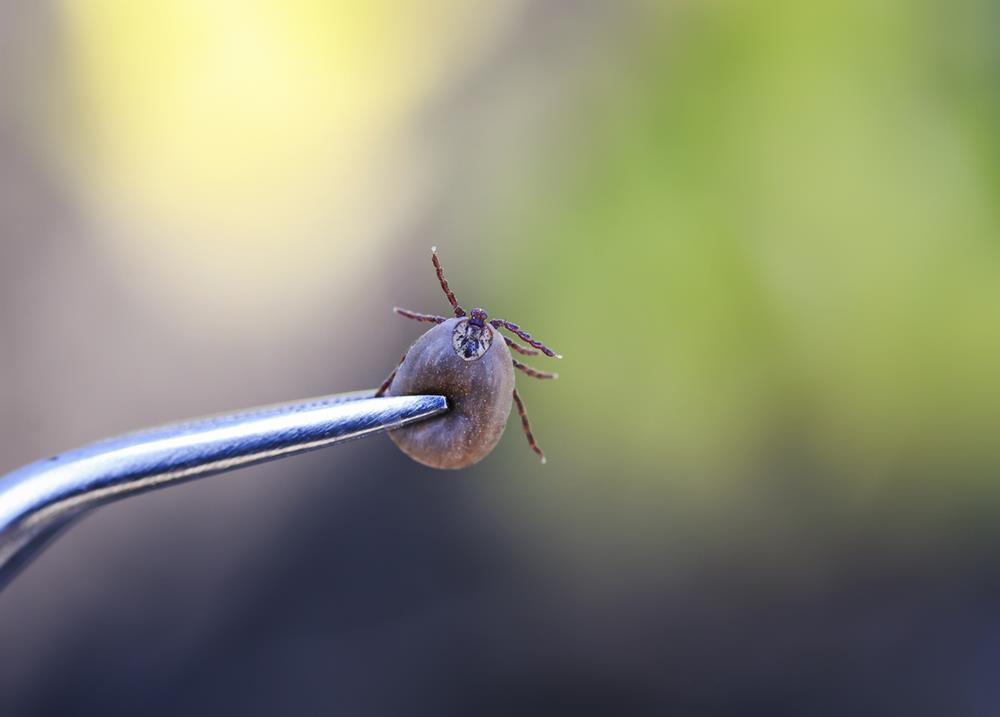

Although ticks are small, their impact on health can be significant, making prevention and safe removal vital. Check yourself, your clothing, and your pets for ticks after outdoor activities, especially in tall grass or wooded areas. This vigilance helps catch ticks before they bite.
To safely remove a tick, use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp it close to your skin and pull upward steadily to avoid leaving parts behind. After removal, clean the bite area and your hands with rubbing alcohol or soap and water. Monitor for tick-borne disease symptoms like fever or rash, which can indicate Lyme disease.
Wear light-colored, tightly woven clothes and consider permethrin-treated garments to reduce tick exposure. Save the tick for identification if symptoms arise.
During a power outage, it is crucial to monitor refrigerator temperatures to ensure food safety, as perishable items left above 40°F for more than two hours can pose health risks.
Mosquito Bite Prevention and Management
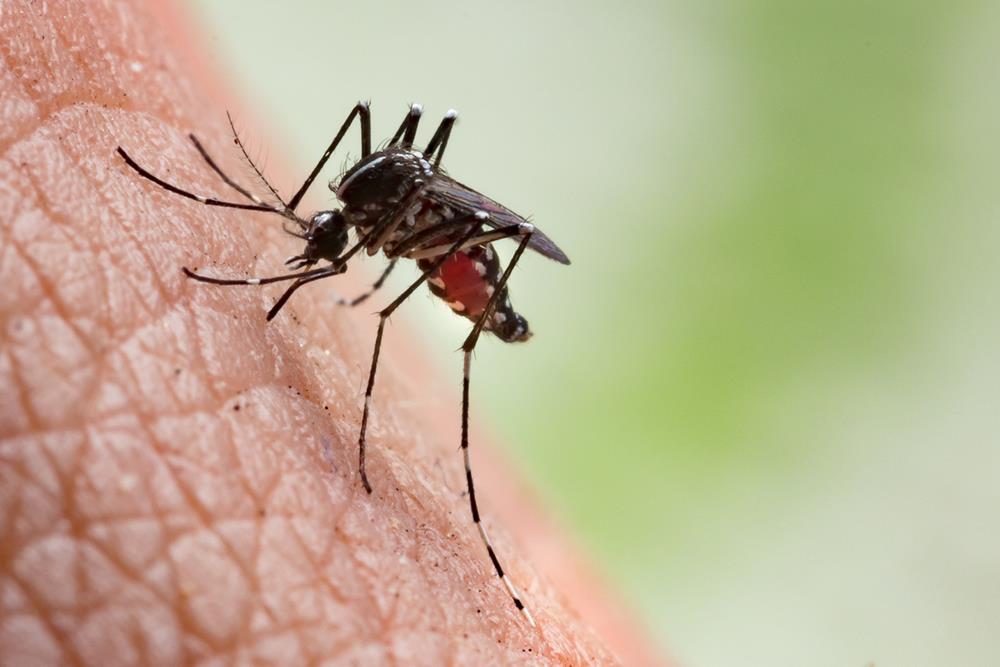
Just as ticks pose a risk to your health, mosquitoes are another small but significant threat, known for spreading diseases like Zika, West Nile virus, and Dengue fever.
Mosquito bite prevention is crucial, especially in post-disaster settings. To protect yourself, apply EPA-approved insect repellents with DEET or Picaridin on exposed skin. Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants to cover up as much as possible.
Eliminate standing water around your home, as mosquitoes breed there. Regularly check and empty containers that collect water. Make sure windows and doors have intact screens to keep mosquitoes out.
Be mindful of peak mosquito activity at dawn and dusk, and plan your outdoor activities accordingly to reduce exposure.
Dealing With Stings From Bees, Wasps, and Hornets
When dealing with stings from bees, wasps, and hornets, staying calm is key to preventing further harm. These insects usually sting when provoked, so avoid swatting at them to reduce the risk of multiple bites and stings.
If you're stung, quickly remove the stinger (for bee stings) by scraping it away with a flat object. Apply ice to the area to reduce swelling and manage pain effectively.
Be aware of your surroundings and avoid nesting sites like eaves and attics to prevent encounters. It's essential to monitor for any signs of an allergic reaction, including difficulty breathing and facial swelling, as these require immediate medical attention.
Staying vigilant helps guarantee your safety in a post-disaster world.
Addressing Allergic Reactions to Bites and Stings
While managing the immediate effects of stings from bees, wasps, and hornets, it's just as essential to recognize and address allergic reactions that might follow. An insect bite can lead to numerous reactions, from normal to serious. A typical bite might resolve in hours, but a large local reaction involves significant swelling and pain, possibly needing prescription relief.
The most serious condition is anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction with symptoms like widespread itching and difficulty breathing, demanding immediate medical attention.
Antihistamines, such as Claritin, can alleviate itching and swelling for less severe reactions. Always monitor symptoms after a bite; if they worsen, seek professional help.
Delayed reactions can indicate serious complications, so don't ignore any changes in your condition.
Travel Tips for Avoiding Insect-Borne Diseases
Before starting on your expedition, it’s crucial to arm yourself with knowledge and preventive measures against insect-borne diseases.
Initially, consult a healthcare provider or travel clinic at least six weeks before your trip. They'll guide you on necessary vaccines or medications tailored to your destination's risks.
Second, research the peak activity times and locations of disease-carrying insects. This will help you plan the safest time outdoors.
Third, don't forget to use EPA-approved insect repellents with DEET or Picaridin.
Here's a quick checklist:
- Vaccines or Medications: Consult your doctor six weeks prior.
- Peak Insect Activity: Know when and where insects are most active.
- Repellents: Apply DEET or Picaridin when spending time outdoors.
Stay informed and protected!